ESG Disclosure for Human Capital
(For Board Chairs, Directors, CEOs, CHROs, COOs, CFOs, CMOs, CROs and Chief Sustainability Officers)

Speakers


















Chief Guest
Ashfaq Yousuf Tola, Member Policy Board at MOPDSI
Renowned economist and Former Minister of State Pakistan Ashfaq Yousuf Tola, FCA, has taken on a new role as a Member of the Policy Board at the Ministry of Planning, Development, and Special Initiatives.
Ashfaq Yousaf Tola, FCA, is a distinguished professional with over 25 years of diverse experience spanning tax planning, assurance, business advisory services, international mergers and acquisitions, corporate finance, investment advisory, due diligence, financial product design and launch, public listings, and corporate affairs.

Why ESG Disclosure?
- Sustainability has emerged as a key challenge and opportunity for every organization. With the emergence of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework, human capital has become important for investment analysis, both from social and financial impact perspective. How “S’ is framed within the ESG, which issues take priority and how they are integrated into the organization’s strategy is a challenge for many companies.
- As the primary source of economy is shifting from physical to intellectual capital, stakeholders realize that company’s true competitive advantage lies in human capital capability. Investors expect board HR Committee, a high-quality workforce data, that can help in better understanding the SOCIAL AND FINANCIAL IMPACT & ROI of human capital investment in MEASURABLE TERMS.
- Numbers are the universal language of business. Organizational leaders. Shareholders, board members, CEOs, CFOs all measure results, therefore, prefer to take decisions on evidence-based data. They are keen to see verifiable connections between human capital investments and leading indicators of organizational sustainability.
- International standards setter institutions and national regulatory bodies are demanding companies to become more transparent, objective and accountable in their investments and corresponding outcomes.
- Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan has published ESG Guidelines for listed companies Link Here
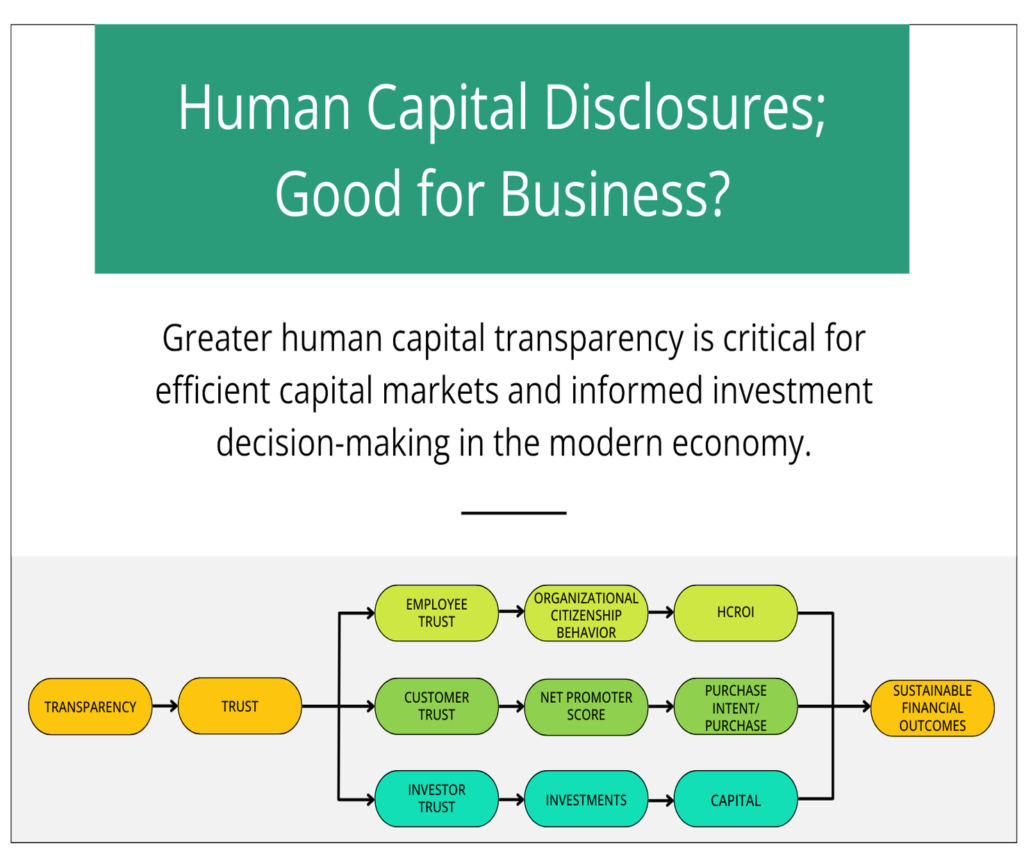
ESG Drives Enterprise Sustainability
Businesses operates within a broader society and industry context. They are deeply intertwined with environmental, social, and governance concerns. Strong ESG proposition creates tangible value for the economy. To continue to thrive, companies need to build their resilience and enhance their capability to operate, through greater commitment to long-term, sustainable value creation that embraces the wider demands of people and planet.
ESG disclosure is an emerging requirement of standards setter bodies, investors, shareholders, donors and regulators. It is essentially required to align the industrial economy with stakeholders’ capitalism concept for sustainable and inclusive growth. To continue to thrive, companies need to build their resilience and enhance their capability to operate, through greater commitment to long-term, sustainable value creation that embraces the wider demands of people and planet.
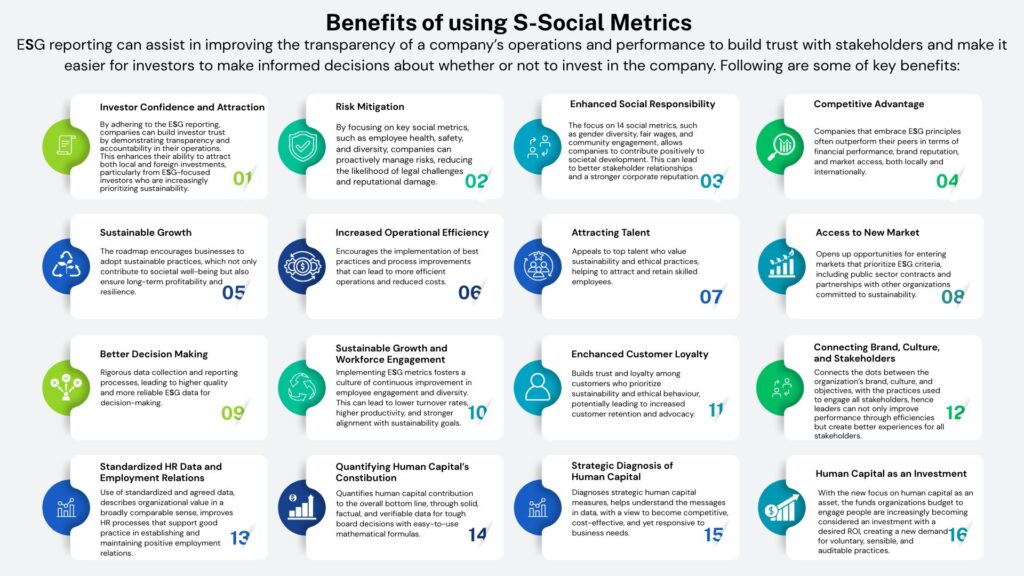
What are the Benefits of using S-Social Metrics
ESG reporting can assist in improving the transparency of a company’s operations and performance to build trust with stakeholders and make it easier for investors to make informed decisions about whether or not to invest in the company. Following are some of key benefits:
1
Investor Confidence and Attraction:
By adhering to the ESG reporting, companies can build investor trust by demonstrating transparency and accountability in their operations. This enhances their ability to attract both local and foreign investments, particularly from ESG-focused investors who are increasingly prioritizing sustainability.
2
Risk Mitigation:
By focusing on key social metrics, such as employee health, safety, and diversity, companies can proactively manage risks, reducing the likelihood of legal challenges and reputational damage.
3
Enhanced Social Responsibility:
The focus on 14 social metrics, such as gender diversity, fair wages, and community engagement, allows companies to contribute positively to societal development. This can lead to better stakeholder relationships and a stronger corporate reputation.
4
Competitive Advantage:
Companies that embrace ESG principles often outperform their peers in terms of financial performance, brand reputation, and market access, both locally and internationally.
5
Sustainable Growth:
The roadmap encourages businesses to adopt sustainable practices, which not only contribute to societal well-being but also ensure long-term profitability and resilience.
6
Increased Operational Efficiency:
Encourages the implementation of best practices and process improvements that can lead to more efficient operations and reduced costs.
7
Attracting Talent:
Appeals to top talent who value sustainability and ethical practices, helping to attract and retain skilled employees.
8
Access to New Market
Opens up opportunities for entering markets that prioritize ESG criteria, including public sector contracts and partnerships with other organizations committed to sustainability.
9
Better Decision Making
Rigorous data collection and reporting processes, leading to higher quality and more reliable ESG data for decision-making.
10
Sustainable Growth and Workforce Engagement
Implementing ESG metrics fosters a culture of continuous improvement in employee engagement and diversity. This can lead to lower turnover rates, higher productivity, and stronger alignment with sustainability goals
11
Enchanced Customer Loyalty
Builds trust and loyalty among customers who prioritize sustainability and ethical behaviour, potentially leading to increased customer retention and advocacy.
12
Connecting Brand, Culture, and Stakeholders:
Connects the dots between the organization’s brand, culture, and objectives, with the practices used to engage all stakeholders, hence leaders can not only improve performance through efficiencies but create better experiences for all stakeholders.
13
Standardized HR Data and Employment Relations:
Use of standardized and agreed data, describes organizational value in a broadly comparable sense, improves HR processes that support good practice in establishing and maintaining positive employment relations.
14
Quantifying Human Capital’s Constibution
Quantifies human capital contribution to the overall bottom line, through solid, factual, and verifiable data for tough board decisions with easy-to-use mathematical formulas.
15
Strategic Diagnosis of Human Capital
Diagnoses strategic human capital measures, helps understand the messages in data, with a view to become competitive, cost-effective, and yet responsive to business needs.
16
Human Capital as an Investment
With the new focus on human capital as an asset, the funds organizations budget to engage people are increasingly becoming considered an investment with a desired ROI, creating a new demand for voluntary, sensible, and auditable practices.
What are the Benefits of using S-Social Metrics
ESG reporting can assist in improving the transparency of a company’s operations and performance to build trust with stakeholders and make it easier for investors to make informed decisions about whether or not to invest in the company. Following are some of key benefits:
Investor Confidence and Attraction: By adhering to the ESG reporting, companies can build investor trust by demonstrating transparency and accountability in their operations. This enhances their ability to attract both local and foreign investments, particularly from ESG-focused investors who are increasingly prioritizing sustainability.
Risk Mitigation: By focusing on key social metrics, such as employee health, safety, and diversity, companies can proactively manage risks, reducing the likelihood of legal challenges and reputational damage.
Enhanced Social Responsibility: The focus on 14 social metrics, such as gender diversity, fair wages, and community engagement, allows companies to contribute positively to societal development. This can lead to better stakeholder relationships and a stronger corporate reputation.
Enhanced Social Responsibility: The focus on 14 social metrics, such as gender diversity, fair wages, and community engagement, allows companies to contribute positively to societal development. This can lead to better stakeholder relationships and a stronger corporate reputation.
Competitive Advantage: Companies that embrace ESG principles often outperform their peers in terms of financial performance, brand reputation, and market access, both locally and internationally.
Sustainable Growth: The roadmap encourages businesses to adopt sustainable practices, which not only contribute to societal well-being but also ensure long-term profitability and resilience.
Increased Operational Efficiency: Encourages the implementation of best practices and process improvements that can lead to more efficient operations and reduced costs.
Attracting Talent: Appeals to top talent who value sustainability and ethical practices, helping to attract and retain skilled employees.
Access to New Markets: Opens up opportunities for entering markets that prioritize ESG criteria, including public sector contracts and partnerships with other organizations committed to sustainability.
Better Decision Making: Rigorous data collection and reporting processes, leading to higher quality and more reliable ESG data for decision-making.
Sustainable Growth and Workforce Engagement: Implementing ESG metrics fosters a culture of continuous improvement in employee engagement and diversity. This can lead to lower turnover rates, higher productivity, and stronger alignment with sustainability goals
Enhanced Customer Loyalty: Builds trust and loyalty among customers who prioritize sustainability and ethical behaviour, potentially leading to increased customer retention and advocacy.
Connecting Brand, Culture, and Stakeholders: Connects the dots between the organization’s brand, culture, and objectives, with the practices used to engage all stakeholders, hence leaders can not only improve performance through efficiencies but create better experiences for all stakeholders.
Standardized HR Data and Employment Relations: Use of standardized and agreed data, describes organizational value in a broadly comparable sense, improves HR processes that support good practice in establishing and maintaining positive employment relations.
Quantifying Human Capital’s Contribution: Quantifies human capital contribution to the overall bottom line, through solid, factual, and verifiable data for tough board decisions with easy-to-use mathematical formulas.
Strategic Diagnosis of Human Capital: Diagnoses strategic human capital measures, helps understand the messages in data, with a view to become competitive, cost-effective, and yet responsive to business needs.
Human Capital as an Investment: With the new focus on human capital as an asset, the funds organizations budget to engage people are increasingly becoming considered an investment with a desired ROI, creating a new demand for voluntary, sensible, and auditable practices.
International Standards and National Regulation on ESG
- ISO 30414: Guidelines for Internal and External Human Capital Reporting (Applicable worldwide to all organizations across all industries).
- ESRS-S1: European Sustainability Reporting Standards for Internal Workforce (Applicable to companies operating within EU or external companies having operations in EU).
- SECP: Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan Guidelines on ESG Disclosure for Listed Companies (Applicable to listed companies in Pakistan on voluntary basis. Non listed companies can also use it).
ISO 30414
ISO 30414: Guidelines for Internal and External Human Capital Reporting. This universal international standard is applicable to organizations of all types across all sectors. It provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for organizations to report 58 metrics related to 11 key areas of human capital management. Number of metrics applicable vary depending upon large/medium/small organization. The Standard provides the first and most widely accepted roadmaps for voluntary, strategic and systematic processes that improve outcomes and experiences. external reporting. It aims to help organizations measure, manage, and report on their workforce effectively, enhancing human governance, transparency and accountability.
ESRS
European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) have been established by the European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG) to guide companies in reporting sustainability-related information. Standards are mandatory for companies within EU or operating in EU on Jan first 2024. These standards aim to provide consistent, comparable, and transparent disclosure on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. ESRS has a special cluster of 17 metrics (S1) for reporting on internal workforce to enhance corporate accountability and objectivity for relevant stakeholders.
SECP
The Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP) has issued voluntary Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Disclosure Guidelines for listed companies. These guidelines aim to promote responsible business practices and transparency amongst listed companies, specifically in light of freshly launched International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) S1 and S2 Standards issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). These standards are supported by a dedicated cluster of 14 Social metrics. These standards are supported by a dedicated cluster of 14 Social metrics. The objective of the SECP ESG Disclosure Guidelines is to encourage companies to report on environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance structures. Companies can integrate ESG information into their Annual Reports or publish it separately.
Goals
HR Metrics is pioneer in Asia for introducing evidence-based human capital measurement Metrics. Our goal is to assist companies in developing their data driven decisions and disclosure capability on human capital with a focus on “S” part of ESG.

ESG Disclosure Benefits
Human capital disclosure metrics help long-term sustainability of enterprise in following ways:
a. Mitigates the risks and enhances opportunities for all stakeholders including shareholders, donors, regulators, employees, compliance agencies, customer and public.
b. Disrupts the way companies think, value and report on their human capital, and delivers what investors look for; sustainable growth and returns.
c. Enhances greater understanding of the financial and non-financial returns that are generated as a result of investments in human capital.
d. Accessible and transparent reporting of human capital data and insights, enhances internal and external understanding and assessment of an organization’s human capital and its present and future performance.
e. Connects the dots between the organization’s brand, culture, and objectives, with the practices used to engage all stakeholders, hence leaders can not only improve performance through efficiencies but create better experiences for all stakeholders.
f. Enables financial investors to credibly assess the quality of HR strategy, action plans and processes of competing companies, include this information in respective financial evaluation models and measure its impact and ROI.
g. Use of standardized and agreed data, describes organizational value in a broadly comparable sense, improves HR processes that support good practice in establishing and maintaining positive employment relations.
h. Quantifies human capital contribution to the overall bottom line, through solid, factual, and verifiable data for tough board decisions with easy-to-use mathematical formulas.
i. Diagnoses strategic human capital measures, helps understand the messages in data, with a view to become competitive, cost effective and yet responsive to business needs.
j. With the new focus on human capital as an asset, the funds organizations budget to engage people are increasingly becoming considered an investment with a desired ROI, creating a new demand for voluntary, sensible and auditable practices.
Focus Areas
1) ESG Awareness
• What is ESG and what is in it for short-term and long-term investors?
• What is the business case for ESG from social and financial outcomes perspectives?
• What are existing global frameworks supporting ESG disclosure and reporting?
• Who are key stakeholders and what is their interest in ESG?
• What is materiality consideration and double materiality for ESG information?
2) ESG Risk Assessment
• What should be role, responsibilities, and structure of board ESG committee?
• How to determine which ESG metrics are material to your business?
• What should be the role of regulators and rating agencies in ESG disclosure?
• What are critical competencies for ESG competent board director?
• Who are ESG competent business leaders globally/regionally?
• How to identify ESG risk for your enterprise?
• How to measure maturing scale of your organization on ESG disclosure?
• How to measure Social (S) in ESG for social and financial impact?
• What are key ESG Metrics for sustainability reporting?
• How to assess enterprise sustainability report for data quality assurance?
3) ESG Enterprise Capabilities
• How to develop ESG strategy for enterprise?
• What resources be consulted to develop ESG strategy?
• ESG seminars on how to write effective ESG annual report?
• ESG certification for consultants and board of directors
• ESG certification for enterprise

Our services
- Consulting
-
- Diagnostic assessment to determine current state.
- Developing strategy to benchmark desired state.
- Developing a dashboard to gather data for report generation.
- Training on metrics definitions, formulas and data points
- Guidance and support on data collection and analysis mechanism
- Writing report for publishing in ESG or annual report
- ISO 30414 Certification
-
- ISO 30414 audit leading to organisational certification.
Note: Organisation has to choose between certification and consulting services. Both cannot be provided to the same company.
Eligibility Criteria for Participation
- Participation is voluntary and without any fee.
- Board director/CEO/CHRO/Chief Sustainability Officer or Chief Risk Officer can join.
How to Get Involved?
- Go to ESG Disclosure page and Register.
- Contact info@thehrmetrics.com to register you.
CEO HR Metrics
Zahid Mubarik is an internationally acclaimed visionary thinker, writer, speaker, thought leader and influencer on human capital analytics, diversity and inclusion. He is the SHRM Partner Pakistan and founding member of ISO Geneva Technical Committee 260 for developing HR global Standards. He actively took part in ISO in-person meetings for developing global HR Standards, organized by American National Standards Institute (Washington DC), British Standards Institute (London), Standards Australia (Melbourne), The Royal Netherlands Standardization Institute (Rotterdam), Association Française de Normalisation (Paris), Singapore Standards Council (Singapore), The National Standardization Agency of Indonesia (Bali) and UNI-Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione (Milan), Canada Standards (Montreal) and Japan Standards (Tokyo).
Zahid served as Global Chair of ISO Working Group on HR Metrics Standards. During his leadership, ISO published two global HR standards including ISO 30410: Impact of Hire and ISO 30411: Quality of Hire. He also served as member of Working Group developing ISO 30414: Guidelines for Internal and External Human Capital Reporting. He facilitated certification of 950+ consultants and practitioners worldwide on ISO 30414 with a heavy concentration in Tokyo Japan. He collaborated with HC Produce Inc Tokyo in certification of 2 companies in Japan on ISO 30414. Zahid has the honour of being a distinguished speaker in international conferences and seminars on human capital analytics at Las Vegas, Beijing, Moscow, Baku, Hanoi, Dubai and Abu Dhabi. His analytical papers and expert talks have been featured by national and international media including CNBC, DAWN, Business Recorder, Business Plus TV, Gulf Economist and Microfinance Gateway World Bank Washington.

Zahid Mubarik
SHRM-SCP, SPHRi, GPHR
President SHRM Forum Pakistan
Member ISO HR Standards Technical Committee 260
Former Member Pakistan Stock Exchange Task Force on ESG
