1. Why ESG is Important?
a. Stakeholder Capitalism
World Economic Forum advocates the principles of “stakeholder capitalism”. This concept is championed for half a century and stated in the Davos Manifesto. International Business Council (IBC) of WEF comprising of 140 CEOs of large corporate is at the forefront of rebalancing of corporate purpose through stakeholder capitalism. IBC has spearheaded a commitment to align their corporate values and strategies with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), to better serve society.
The essence of stakeholder capitalism is that it is the capacity of the private sector to harness the innovative, creative power of individuals and teams to generate long-term value for shareholders, for all members of society and for the planet we share. It is an idea whose time has come. There is an emerging consensus among companies that long-term value is most effectively created by serving the interests of all stakeholders including shareholders, donors, customers, employees, public, government and regulators.


b. Business Roundtable
On August 19, 2019, 181 CEOs of America’s largest corporations overturned a 22 years old policy statement that defined a corporation’s principal purpose as maximizing shareholder return. The CEOs of business roundtable adopted a new statement on the purpose of a corporation declaring that companies should serve not only their shareholders but also deliver value to their customers, invest in employees, deal fairly with the suppliers and support the communities in which they operate. Click here to read more about Business Roundtable.
c. Standards Setter Organizations
To rethink sustainability of this planet, tectonic ESG focused developments are taking place around the world.
a. The European Commission has revisited its Non-Financial Reporting Directive and published Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive.
b. The International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) has accelerated the harmonization of sustainability standards.
c. The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has amended its rules to enhance human capital disclosures.
d. The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation is consulting on broadening its mandate to include sustainability issues.
e. The International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) has called for the creation of an International Sustainability Standards Board to sit alongside the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) under the auspices of the IFRS Foundation.
f. Meanwhile, the leading voluntary framework and standard setters including Climate Disclosure Project (CDP), the Climate Disclosure Standards Board (CDSB), the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) have for the first time committed to work towards a joint vision of ESG.
All above developments form the natural building blocks of a single, coherent, global ESG reporting system for sustainability of corporate value creation system.


2. Why ESG ADVOCACY ?
Businesses operates within a broader society and industry context. They are deeply intertwined with environmental, social, and governance concerns. Strong ESG proposition creates tangible value for the economy. To continue to thrive, companies need to build their resilience and enhance their capability to operate, through greater commitment to long-term, sustainable value creation that embraces the wider demands of people and planet.
Securities & Exchange Commission of Pakistan has published Draft Guidelines on ESG Disclosures for Listed Companies 2023 on 27 Oct 2023.These guidelines are subject to comments review and final approval.
European Union has also passed a law on ESG Disclosure on 31 July 2023. It is called CORPORATE SUSTAINABILITY REPORTING DIRECTIVE. It has created EUROPEAN SUSTAINABILITY REPORTING STANDARDS (ESRS) for formal disclosure reporting for companies operating in EU or any company having subsidiary in EU. It is expected that rest of the world will follow this law as best practice.

The E in ESG, environmental criteria, includes the energy that companies consume and the waste they discharge, the resources they need, and the consequences for living beings as a result. E encompasses carbon emissions and climate change. Every company uses energy and resources; every company affects, and is affected by, the environment.
S, social criteria, addresses the relationships companies have and the reputation they foster with people and institutions in the communities where they do business. S includes human capital relations and diversity and inclusion.


G, governance, is the internal system of practices, controls, and procedures companies adopt to govern themselves, make effective decisions, comply with the law, and meet the needs of external stakeholders. Just as ESG is an inextricable part of how business is conducted, its individual elements are themselves intertwined. Social criteria overlap with environmental criteria and governance when companies seek to comply with environmental laws and broader concerns about sustainability.
HR Metrics has launched ESG ADVOCACY. Purpose of this ADVOCACY is to enhance understanding of ESG information, identify ESG risks and its impact on organizations, manage risks, improve decision making, foster stakeholders’ engagement, promote transparency and accountability at institutional level. ESG ADVOCACY will play a critical role in promoting long-term value creation, risk management, and stakeholder engagement, while enhancing the company’s reputation as a responsible corporate citizen.
Existing Global Frameworks supporting Disclosure Requirements
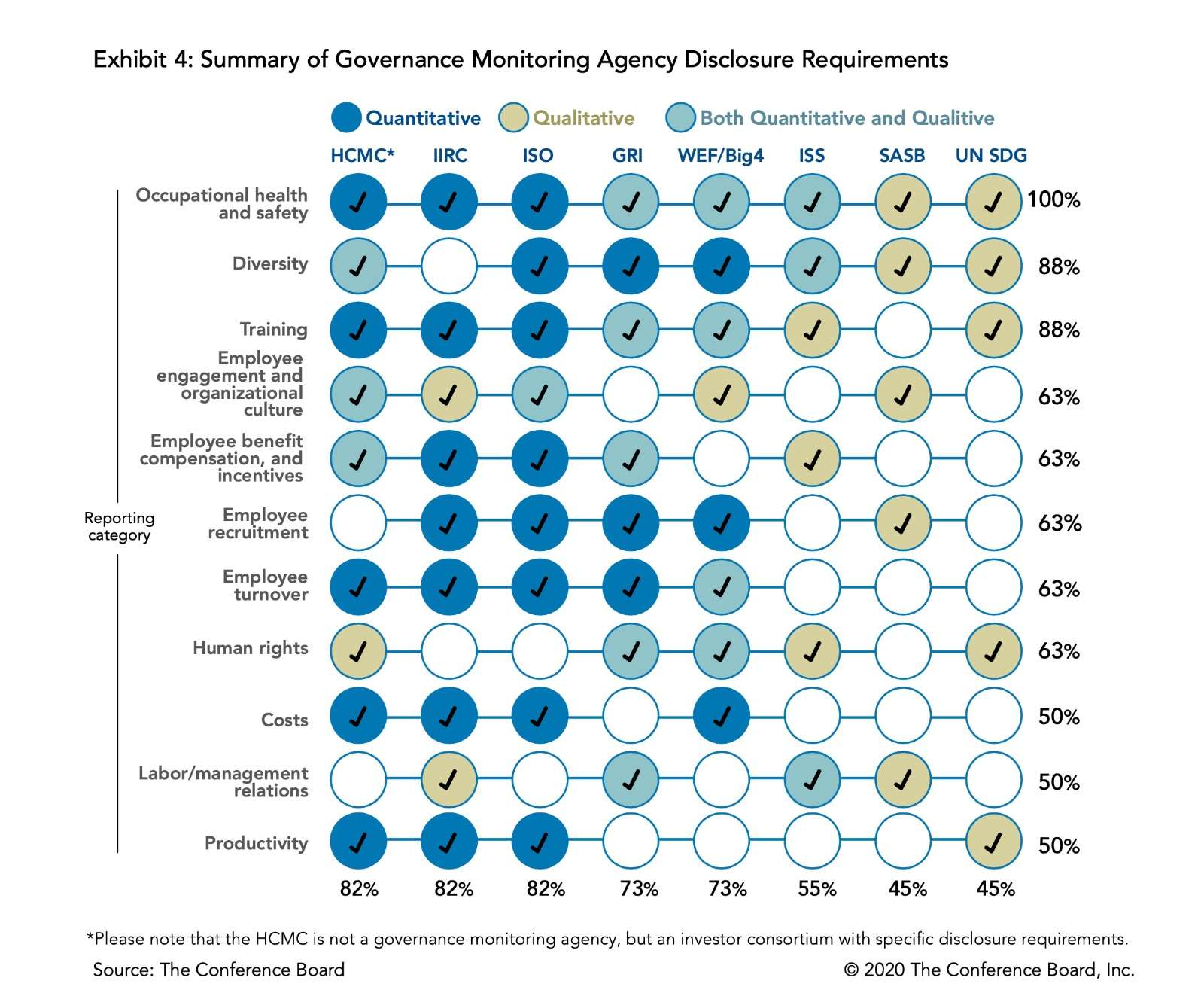
3. What are the goals?
a. Promote Transparency and Accountability to Build Inclusive Economy: ESG ADVOCACY has greater transparency and accountability by providing a platform for all stakeholders to discuss and report on the ESG performance. Which in return helps to build trust with stakeholders and enhance the enterprises and industry reputation as a responsible corporate citizen.
b. Build and Sustain Partnerships ESG ADVOCACY helps in building relationship with legislators, policy makers, society leaders, business leaders, media, government, non-governmental organizations, businesses and academic institutions to address ESG challenges that influence the effectiveness and sustainability of their organizations and communities.
c. Serve as an Advocate ESG ADVOCACY ensure that policy makers, law makers and regulators are aware of key ESG concerns being faced by organizations and communities.

d. Enhance Understanding of ESG Issues: The ESG ADVOCACY serves as a platform to deepen the understanding of ESG issues and their impact on the company’s operations, reputation, and financial performance.
e. Identify and Manage ESG Risks: By discussing ESG risks and opportunities in a structured manner, ESG ADVOCACY helps stakeholders in identifying emerging risks, assess their potential impact, and develop strategies to manage them effectively.
f. Improve Decision-Making: ESG ADVOCACY facilitates the integration of ESG considerations into the overall decision-making processes. By discussing ESG issues, decision makers can make better-informed decisions that take into account the organizations long-term sustainability and stakeholder interests.
g. Foster Stakeholder Engagement: ESG ADVOCACY provides a platform for board of directors to engage with stakeholders on ESG issues. By engaging with stakeholders, the board can gain insights into their perspectives and concerns, which can inform the company’s ESG strategy and decision-making.
4. What issues will be discussed?
Discussion topics will depend on the specific needs and goals of the members however following is a suggestive but not exhaustive list of topics.
Environmental issues
This aspect address the issue of climate change, resource depletion, pollution, waste management, and biodiversity loss.
Social issues
Explores the opportunity area for improving workforce practices, human rights, diversity and inclusion, community relations, and product safety.
Governance issues
The broader issue of board structure and composition, executive compensation, audit risk management and stakeholders’ engagement.
ESG reporting and disclosure
It provides the reporting frameworks, metrics, and best practices for disclosing ESG information to stakeholders.
Industry-specific ESG issues
It explores the specific issues to the industry in which the organization operates, such as supply chain management in the retail industry, water usage in the agriculture industry, or data privacy in the technology industry.
ESG integration into business strategy
The integration of how ESG considerations are integrated into the organization’s overall strategy and decision-making processes.
Emerging ESG issues
The new and emerging ESG issues that are likely to impact the organization in the future, such as emerging technologies, changing consumer preferences, or regulatory developments.
5. Our Services
ESG ADVOCACY will assist members in developing their knowledge & skills in following areas.
1. ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT
a. ESG awareness
• What is ESG and what is in it for short-term and long-term investors? • What is the business case for ESG from social and financial outcomes perspectives? • What are existing global frameworks supporting ESG disclosure and reporting? • Who are key stakeholders and what is their interest in ESG? • What is materiality consideration and double materiality for ESG information?
b. ESG risk assessment
• What should be role, responsibilities, and structure of board ESG committee? • How to determine which ESG metrics are material to your business? • What should be the role of regulators and rating agencies in ESG disclosure? • What are critical competencies for ESG competent board director? • Who are ESG competent business leaders globally/regionally? • How to identify ESG risk for your enterprise? • How to measure maturing scale of your organization on ESG disclosure? • How to measure Social (S) in ESG for social and financial impact? • What are key ESG Metrics for sustainability reporting?
c. ESG Enterprise Capabilities
• How to develop ESG strategy for enterprise. • What resources be consulted to develop ESG strategy? • ESG seminars on how to write effective ESG annual report? • ESG certification for consultants and board of directors. • ESG certification for enterprises.
2. ENTERPRISE ASSESSMENT ON ESG DATA QUALITY ASSURANCE
- Assess enterprise sustainability reports for data quality assurance.
3. ENTERPRISE AWARDS FOR ESG DISCLOSURE
- Conduct annual “Stakeholder Capitalist Award for Sustainable Disclosure.
- ESG publication to communicate best practices.
6. ESG ADVOCACY Think Tank
HR Metrics will form a Think Tank of highly renowned society leaders with following criteria.
a. Influential legislators, policy makers and society leaders, having passion, tenacity and drive toward ESG results.
b. Values and behaviours that align with ESG mission and objectives.
c. Be proactive with ideas, engaging others, participating and speaking in events.
d. Willing to share ESG trends, experiences, challenges, opportunities and success stories.
e. Serve without compensation. Likewise, no expectation of monetary contribution.
f. Participate in 2 hours meeting per quarter. Option to join virtually or in person.
g. Date/venue of meeting to be decided with member’s consent.
h. Membership term is 2 years, extendable to 1 more term.
7. Who are eligible for membership?
a. Legislators, Policy Makers
b. Investors, Shareholder
c. Corporate Board Chairs
d. Board Directors, CEOs, Head of Institutions.
e. C-suite (COOs, CFOs, CHROs, CMOs, CIOs, CRO, CCO).
f. Consultants, Trainers
g. Academicians, Researchers
h. Professionals
i. Membership is free for first 3 months starting 1 Dec 2023-28 Feb 2024.
j. Terms of engagement for subsequent membership will be shared later.
8. Timelines
a. ESG capabilities and competencies survey: 16 Nov – 31 Dec 2023
b. Report publication: 25 Jan 2024
c. Activation of ESG ADVOCACY operations: 1 Jan-30 Apr 2024
d. National Awards & Conference on Sustainability Disclosure: 14 Oct 2024
Questions/Comments to Zahid Mubarik
CEO HR Metrics Zahid@thehrmetrics.com
E$G ADVOCACY Convenor
Zahid Mubarik is an internationally acclaimed visionary thinker, writer, speaker, thought leader and influencer on human capital development, analytics, diversity and inclusion. He is the founding member of ISO Geneva Technical Committee 260 for developing HR global Standards. He actively took part in ISO face to face meetings for global HR Standards development at American National Standards Institute (Washington DC), British Standards Institute (London), Standards Australia (Melbourne), The Royal Netherlands Standardization Institute (Rotterdam), Association Française de Normalisation (Paris), Singapore Standards Council (Singapore), The National Standardization Agency of Indonesia (Bali) and UNI-Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione (Milan). Zahid has the honor of being distinguished speaker in international conferences and seminars on human capital analytics at Las Vegas, Beijing, Moscow, Baku, Hanoi, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Tokyo. His analytical papers and expert talks have been featured by national/international media including Microfinance Gateway World Bank Washington, CNBC, Dawn, Business Recorder, Business Plus TV and Gulf Economist.
Zahid served as Global Chair of ISO Working Group on HR Metrics Standards. During his leadership, ISO published two global HR standards including ISO 30410: Impact of Hire and ISO 30411: Quality of Hire. He also served as member of Working Group developing ISO 30414: Guidelines for Internal and External Human Capital Reporting. He groomed and facilitated certification of 500+ consultants/practitioners worldwide with a heavy concentration in Tokyo Japan. Zahid is SHRM USA Partner in Pakistan. SHRM is world largest HR association having 325,000+ members in 165 countries. He introduced SHRM competency based global HR certifications in Pakistan and developed more than 200 people. He served as Board Director The Centre for Global Inclusion USA. He introduced Global Diversity, Equity & Inclusion Benchmarks Standards in Pakistan and facilitated 65 large multinational and national corporations in implementing Global DEI Benchmarks Standards. Zahid is a member of Pakistan Stock Exchange and Pakistan Institute of Corporate Governance Task Force on ESG Disclosure. He has a knack in using human capital analytics to transform organization on (S-Social) part of ESG. He is the Chief Editor of HR Magazine Workforce Tomorrow.


